
Spinning Fire: A Guide to Steel Wool Photography
I think steel wool photography creates some of the most amazing images you can capture
Share the Love This Valentine’s Day – 25% Off


What is the stacked sensor advantage in modern digital cameras? Stacked CMOS sensors are revolutionizing the field of digital photography. What makes this technology relevant? How does this new design lead to improvements in how cameras work?
This change is huge; when light hits these special pixels, data moves quickly. Faster shots, less noise in low light, and improved image clarity are the outcomes.
Stacked CMOS sensors offer numerous advantages. First, they are a layered design separating light capture from processing. This enhances their efficiency in managing light.
These sensors are faster, less noisy, and have better light sensitivity. Hence, your camera performs better in various situations. Whether it’s rapid action, tough lighting, or detailed landscapes, stacked sensors help.
Engineers have separated photodiodes from circuitry, which reduces interference. This separation results in the production of crisper photos and more accurate colours.
The photodiode layer focuses on light capture, while the circuitry handles data. This setup ensures each function works best without interference. Signals travel vertically, reducing noise and preserving clarity.
Your photos capture more detail; they’ll look more natural in tough shooting conditions. You’ll notice sharper edges and more vibrant colours.
BSI technology boosts light capture in image sensors. In traditional sensors, wiring blocks some light. BSI places photodiodes at the top to catch more light. It boosts quantum efficiency, converting a greater number of photons into electrical signals.
It means better light sensitivity and performance. BSI and stacked designs work together to enhance efficiency.
By reducing heat and noise, you can shoot at higher ISO without sacrificing image quality. This is a game-changer for night scenes and indoor events.
Improve autofocus in low light, making them ideal for night photography and astrophotography. You can take handheld shots in dimly lit places without a tripod.
Download your free trial today!
They offer big improvements over traditional CMOS technology. These changes make them perfect for high-performance cameras.
Stacked CMOS sensors have a different design than traditional ones. In traditional sensors, light-capturing photodiodes and circuitry are on the same layer. This design limits how well the sensor can work.
Stacked sensors, on the other hand, separate these elements into different layers. Photodiodes are on one layer, and circuitry is on another. Tiny vertical connections known as through-silicon vias (TSVs) accomplish this separation.
This layered design has big advantages. It lets manufacturers focus on each layer’s function. The photodiode layer can catch more light, while the circuitry layer can be more complex without getting in the way.
| Features | Convential CMSO | Stacked CMOS | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Structure | Single layer design with photodiodes and circuitry sharing space | Multi-layer design with separated photodiodes and processing circuitry | More efficient use of sensor real estate |
| Readout Speed | Typically 1/15 to 1/30 second for high-resolution sensors | As fast as 1/200 second even at high resolutions | Reduced motion artifacts, faster burst shooting |
| Processing Power | Limited by space constraints on single layer | Enhanced with dedicated processing layer and integrated memory | More sophisticated in-sensor processing capabilities |
| Dynamic Range | Typically 10-12 stops | Can exceed 15 stops with advanced ADC | Better highlight and shadow detail retention |
A normal CMOS sensors read data row by row, slowing data flow. This generates “rolling shutter” distortion of moving objects. Sensors stacked are quicker. Processing data faster because of their dedicated processing layer and memory.
Rolling shutter artifacts are reduced, making electronic shutters preferable for moving subjects. Many cameras can shoot 20-30 frames per second, making continuous photography faster.
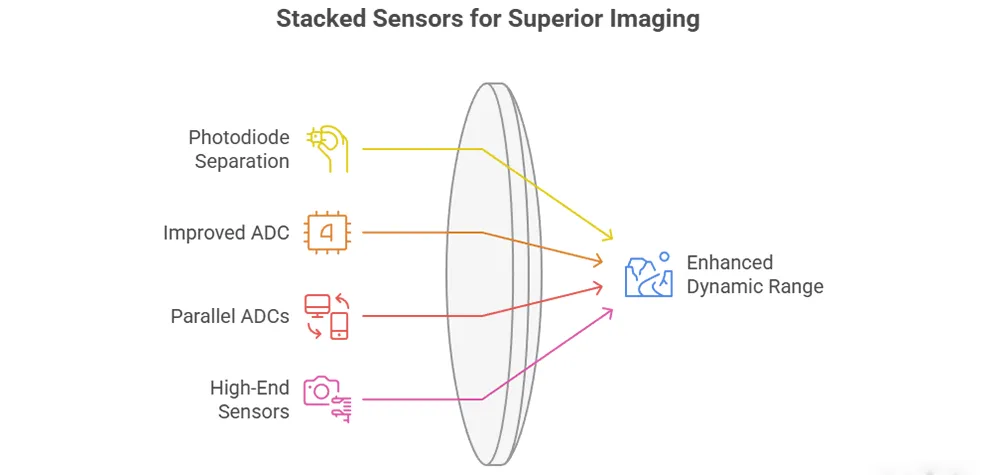
Dynamic range (HDR) is the ability to capture both bright and dark areas in an image. Stacked sensors work better by separating photodiodes from circuitry. This enables improved analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and on-chip processing.
Because ADCs and photodiodes share space, traditional sensors have little dynamic range; ADCs on their layer prevent this.
This configuration improves photodiode signal processing. Many stacked CMOS sensors employ parallel ADCs with several converters. Minimizes noise and improves digital precision.
Expanding the dynamic range helps landscape and studio photographers by capturing more detail. Some high-end stacked sensors have 15 stops of dynamic range, compared to 12-13 for standard sensors.
Knowing how shutters work with stacked CMOS sensors is key to getting the most from your camera. The shutter you pick can greatly affect your photos, making them better for fast-moving subjects. Stacked sensors bring big benefits, but these vary with each shutter type.
Global shutters take a picture all at once, exposing every part of the image at the same time. This is a big plus over rolling shutters, which scan line by line.
Here are some key benefits of global shutters:
Global shutters work best with stacked CMOS sensors. This combo is great for sports and wildlife photos, where you need to freeze moments perfectly.
Electronic shutters don’t move parts to control exposure; they turn photosites on and off electronically.
Stacked sensors have photodiodes and circuitry in separate layers; hence, cameras read the data faster.
This fast data flow means better burst shooting and autofocus. It also reduces lag, making your camera more responsive.
Rolling shutter distortion happens when different parts of an image are captured at different times. This can cause visual problems in your photos.
Stacked sensors help with these issues by reading data faster. Even in extremely fast scenes, they reduce distortion so much it’s almost invisible.
Looking to stretch your budget? We’ve got good news! Save an additional 10% use code bwild10
The latest breakthroughs in stacked sensor are changing how cameras capture and process photos. These advancements are more than just small improvements. They represent big changes in how digital cameras work. With each new generation, stacked sensors offer abilities that were once impossible.
Camera makers are racing to make better stacked sensors. These advanced parts are now key for top models. They give photographers fast speeds and better image quality. The addition of special processing layers in the sensor stack opens up new possibilities for photography.
Canon and Nikon are leading the way in stacked sensor development. Each company has its approach. Canon’s EOS R3 has a stacked CMOS sensor for professionals. It reads out data fast, reducing distortion and allowing for smooth shooting at 30 frames per second.
Canon’s image processor works closely with the sensor. This makes data transfer faster and processing more efficient. Their Dual Pixel CMOS AF technology also works well with the stacked design. It tracks subjects accurately, even in tough lighting.
Nikon’s Z9 camera has a stacked sensor without a mechanical shutter. It uses the electronic shutter for all shots, without sacrificing image quality. This is thanks to advances in sensor design that cut down readout times.
Both companies have moved beyond traditional Bayer colour filters in their top sensors. These new patterns improve colours and light sensitivity. The competition between them speeds up the development of new sensor tech.
I believe resolution will keep going up, but with a focus on more dynamic range. Future sensors will have variable gain technology, which will improve both bright and dark areas in one shot, removing the need for a neutral density filer in landscape photography.
Sensors with built-in memory layers are also on the horizon. These will store data fast, allowing for more shots without a buffer. Some prototypes can shoot thousands of frames per second.
Video and still photography will blend together more. Stacked sensors will enable 8K video without overheating.
Traditional silicon sensors are reaching their limits. New materials like gallium arsenide could improve light capture. They might even extend sensitivity to near-infrared without filters.
Graphene-based sensors are another area of research. This thin carbon material could greatly improve light sensitivity. Early tests show it can capture images in very low light.
Organic semiconductors are also being explored. They can be tuned for specific light wavelengths. This could make sensors more light-sensitive and colour-accurate.
| Semiconductor materials | Key Advantages | Current Development | Potential Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon (Current Standard) | Well-established manufacturing | Mature technology | All current digital cameras |
| Gallium Arsenide | Extended spectral sensitivity | Early commercial testing | Low-light and scientific imaging |
| Graphene | Extraordinary light sensitivity | Laboratory prototypes | Night vision and astronomy |
| Organic Semiconductors | Wavelength-specific sensitivity | Research phase | Colour-accurate professional cameras |
New materials aren’t just replacing silicon. They’re being used as special layers in hybrid sensors. Example, silicon might handle light capture, graphene electron transfer, and organic semiconductors colour. This mix uses each material’s strengths.
Using these new materials is a challenge, but the benefits are worth it. As production gets better, we’ll see these materials in high-end cameras first. Then, they’ll become common in all photography gear.
Stacked sensors have changed digital photography in many ways. They solve specific problems for each camera type. This technology has improved camera performance and size for both pros and casual users.
Mirrorless cameras have seen big improvements with stacked sensors. Without the mechanical mirror, designers could focus on new challenges.
One big win is in continuous shooting. Mirrorless cameras with stacked sensors can shoot 20-30 frames per second. This is a huge jump from before.
Electronic viewfinders also get a boost. They show images almost instantly, making them feel like optical viewfinders. Video quality also improves, with less distortion and better heat control.
Full-frame cameras used to struggle with their size. They had to process more data, making them slower. Stacked sensors fix this problem.
With stacked sensors, full-frame cameras can process data faster. This means they can handle high resolutions without slowing down. It’s a big win for pros.
Heat was another problem for large sensors. Cameras can now shoot for longer without losing quality.
Smartphones have seen huge changes with stacked sensors. These designs fit perfectly in tight spaces. It’s a big advantage for your smart phones photography. Your top smartphones now have better cameras thanks to stacked sensors.
So, what does all this mean for the average photographer? In simple terms, stacked CMOS sensors enable your camera to perform more tasks and do them faster and better. You’ll notice quicker autofocus, clearer photos in tricky lighting, and less distortion when shooting fast-moving subjects.
Whether you’re capturing a night scene, a busy sports game, or a quiet landscape, your camera is more likely to keep up and deliver sharp, detailed images. You don’t need to be a tech expert to benefit from this; stacked sensors just make everyday photography easier and more reliable.

I think steel wool photography creates some of the most amazing images you can capture

Long exposure photography is a technique that uses slow shutter speeds to capture silky smooth

The first time I went to the Medicine Bowls in Courtenay, it felt like a